If you’re new to sewing or DIY projects, you might wonder what is cotton fabric and why so many people choose it. Cotton fabric comes from the soft, fluffy fibers around the seeds of the cotton plant.
It feels gentle on your skin and stays cool, making it a favorite for all ages. You’ll see cotton everywhere, from T-shirts to home décor, because it’s strong, easy to work with, and comfortable.
- Global cotton production reaches about 25 million tonnes each year.
- Cotton accounts for nearly a quarter of global fiber production.
- Over half of all cotton produced ends up in clothing, showing just how much everyone loves cotton fabric.
If you’re curious about what cotton fabric is and why it matters, you’re in the right place.
Key Takeaways
- Cotton fabric comes from the soft fibers around cotton seeds and has been used for thousands of years due to its comfort and strength.
- Cotton is soft, breathable, durable, and highly absorbent, making it ideal for clothing, home textiles, and DIY projects.
- The production of cotton fabric involves careful farming, cleaning, spinning, weaving, and finishing steps that combine tradition with modern technology.
- Different types of cotton fabric, like muslin, poplin, denim, and sateen, offer unique textures and uses for various projects.
- Choosing certified and sustainably produced cotton helps protect the environment, and simple care steps keep cotton items soft and long-lasting.
What is Cotton Fabric?

Definition
When you ask, “What is cotton fabric?” you’re really exploring a story that stretches back thousands of years. Cotton fabric comes from the fluffy fibers that grow around the seeds of the cotton plant.
These fibers are single plant hairs, each one a tiny cell that develops on the seed’s surface. When you see a cotton boll burst open in the field, you’re looking at the raw material for one of the world’s most popular textiles.
People have used cotton fabric since ancient times. Archaeologists have found cotton threads and cloth fragments in places like the Indus Valley, Egypt, and Peru, dating back as far as 5000 BC.
The word “cotton” itself comes from the Arabic word “qutn,” showing how trade and culture helped spread this natural fiber across continents. Over time, different regions domesticated their own cotton species, which led to a rich variety of cotton fabrics.
Here’s a quick look at the roots of cotton fabric:
| Evidence Type | Description | Date/Period | Location/Origin |
|---|---|---|---|
| Earliest cotton fibers | Cotton fibers found at Tel Tsaf, the earliest known in the Near East | ~5200 BCE | Tel Tsaf, Jordan Valley |
| Early cotton use | Cotton fiber threads are used to string copper beads | 6,000-5,500 BC | Mehrgarh, Indus Valley |
| Earliest cotton fabric | Small cloth fragment on silver vase lid | 3,000-2,750 BC | Mohenjo-Daro, Indus Valley |
| Domestication hypothesis | Seed evidence suggests domestication during the Harappan civilization | 2,600-1,900 BC | Indus Valley |
So, what is cotton fabric? It’s a textile made by spinning and weaving the seed fibers of the cotton plant. These fibers are mostly cellulose, which gives the cotton fabric its strength and softness. You’ll find cotton fabric in everything from T-shirts to quilts, and it remains a favorite for its comfort and versatility.
F&A stands out in the DIY fabric world by blending this deep-rooted tradition with modern innovation. Since 2013, F&A has inspired crafters and designers with high-quality cotton fabrics that honor both heritage and creativity.
Key Features
You might wonder why cotton fabric is so popular. The answer lies in its unique features, shaped by both nature and technology. Let’s break down what makes cotton fabric special:
- Softness and Comfort: Cotton fabric feels gentle against your skin. The natural structure of the fiber creates a soft, breathable material that keeps you cool in summer and cozy in winter.
- Durability: Cotton fabric stands up to daily wear and washing. The cellulose-rich fibers give it strength, so your favorite cotton shirt or bedsheet lasts longer.
- Absorbency: Cotton can absorb up to 27 times its weight in water. This makes it perfect for towels, bathrobes, and summer clothes that need to wick away moisture.
- Breathability: Air flows easily through cotton fabric, which helps regulate your body temperature. You stay comfortable, even on hot days.
- Versatility: You can dye, print, or finish cotton fabric in countless ways. Traditional methods like fermentation and sun-drying create beautiful, lasting colors. Modern techniques—like digital printing and enzyme-based processing—add precision, speed, and eco-friendliness.
- Sustainability: Cotton is a natural fiber, and new farming methods focus on reducing water use and chemical inputs. Precision agriculture, drip irrigation, and sustainable dyeing help make cotton fabric a greener choice.
- Innovation: Today’s cotton fabric can do more than ever. Nanotechnology adds antibacterial and UV-protective properties. Smart cotton fabrics can even monitor your health or adjust to temperature changes.
Tip: F&A uses advanced spinning, weaving, and printing technologies to create cotton fabrics that are not only beautiful but also sustainable and high-performing. Their fabrics combine the best of tradition and modern science, making them a top pick for DIY projects.
When you choose cotton fabric, you’re picking a material with a rich history, proven comfort, and exciting new possibilities. Whether you’re sewing a dress, quilting a blanket, or crafting something unique, cotton fabric gives you the perfect blend of tradition and innovation.
How is Cotton Fabric Made?

Ever wondered how a fluffy cotton boll turns into the soft cotton fabric you love? The journey from field to finished fabric is a fascinating mix of tradition, science, and innovation. Let’s walk through each step so you can see exactly how is cotton fabric made—from the soil to your sewing table.
Cultivation and Harvesting
Cotton production starts in the field. Farmers prepare the soil with care, making sure it’s healthy and ready for planting. Here’s a quick look at the main steps:
- 1. Soil Preparation and Planting: Farmers test the soil, plow deeply, and create raised beds. They plant cotton seeds when the soil warms up, spacing them out to help each plant grow strong and healthy.
- 2. Water Management: Cotton needs the right amount of water. Many farms use drip or sprinkler irrigation to save water and keep the plants happy, especially during key growth stages like flowering and boll formation.
- 3. Nutrient Management: Balanced fertilizers and organic compost boost plant health and increase yields. Farmers often split fertilizer applications to match the plant’s needs.
- 4. Weed and Pest Control: Integrated weed and pest management keeps the fields clean and the plants safe. Some growers use natural predators or resistant cotton varieties to reduce chemical use.
- 5. Harvesting: When the bolls burst open, it’s time to pick the cotton. Some farms use machines for speed, while others pick by hand for the best quality. Careful harvesting keeps the fiber long and clean.
Did you know? Sustainable cotton production uses precision agriculture, drip irrigation, and even drones to monitor crops. These methods help save water, reduce chemicals, and protect the environment.
F&A supports sustainable farming by sourcing cotton from growers who use eco-friendly and efficient practices. This commitment ensures that every yard of cotton fabric starts with responsible cotton production.
Ginning and Carding
After harvesting, the cotton heads to the gin. Here, machines separate the valuable fiber from the seeds and any leftover plant material. Clean, fluffy fiber is the goal—this is what will become cotton fabric.
- Ginning: The gin removes seeds and debris, leaving behind pure cotton fiber. This step is crucial for quality. Clean fiber means stronger, smoother yarn later on.
- Carding: Next, carding machines comb the fiber, aligning the strands and removing any remaining impurities. This process creates soft, continuous slivers ready for spinning.
F&A uses advanced ginning and carding equipment to ensure every batch of cotton fiber meets strict quality standards. Automated systems and real-time monitoring help reduce waste and keep the process efficient.
Spinning and Weaving
Now the magic really begins. The clean, carded fiber moves to the spinning room, where it transforms into yarn. Here’s how it happens:
- Spinning: Machines twist and stretch the fiber into long, strong yarns. Modern spinning uses computerized controls to adjust speed and tension, making sure every yarn is consistent and high-quality. Automation also cuts down on errors and waste.
- Weaving or Knitting: The yarn heads to high-speed looms or knitting machines. These machines weave the yarn into fabric by interlacing threads in precise patterns. Digital controls allow for quick design changes and help prevent defects.
Tip: F&A’s state-of-the-art spinning and weaving facilities use over 1,000 airjet looms and advanced robotics. This technology boosts productivity, lowers costs, and delivers beautiful, reliable cotton fabric for your DIY projects.
With these innovations, F&A can offer a wide range of cotton fabric styles, from classic weaves to custom prints, all while keeping quality and efficiency high.
Finishing
The last step in how cotton fabric is made is finishing. This stage gives the fabric its final look, feel, and performance.
- Pre-Treatment: The fabric goes through processes like scouring and bleaching to remove natural oils and prepare it for dyeing.
- Dyeing and Printing: Eco-friendly dyes and advanced printing methods add color and patterns. Waterless dyeing and digital printing help save water and reduce pollution.
- Special Treatments: Finishing can add softness, water repellency, or even antibacterial properties. F&A uses non-toxic treatments and energy-efficient machinery to keep the process safe for you and the planet.
- Quality Control: Every yard of cotton fabric passes through strict inspections. F&A’s professional team checks for color, strength, and consistency, making sure you get only the best.
Note: F&A’s commitment to sustainability shines in the finishing process. They recycle water, use safe chemicals, and follow international standards like OEKO TEX to protect both people and the environment.
From the field to the final inspection, each step in cotton fabric production combines tradition, technology, and care. When you choose F&A, you support a process that values quality, sustainability, and creativity at every stage.
Cotton Fabric Properties
Softness and Breathability
When you touch cotton fabric, you notice how soft and gentle it feels. This comfort comes from the natural structure of cotton fibers. They are smooth and reduce friction, so your skin stays happy—even if you have sensitive skin or allergies.
You might love wearing cotton T-shirts or using cotton sheets because they let your skin breathe. The airy fiber structure allows air to move freely, which keeps you cool in summer and cozy in winter.
- Cotton is naturally soft and gentle on the skin.
- The smooth texture helps prevent irritation.
- Airy fibers allow for excellent breathability.
- Cotton traps less heat and moisture than synthetic fabrics.
- Certified organic cotton avoids harsh chemicals, making it even safer for you.
Compared to polyester or other synthetics, cotton fabric is less likely to cause irritation or trap sweat. That’s why you often see cotton used for baby clothes and summer outfits.
Durability
You want your favorite cotton fabric items to last, even after many washes. Cotton fibers are strong and can handle daily wear.
Studies show that pure cotton fabrics keep most of their strength after 100 washes, with only up to a 30% reduction in tensile strength. Blends with polyester hold up even better, but pure cotton is easier to recycle and feels softer.
| Fabric Type | Washing Cycles Tested | Tensile Strength Retention (%) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pure Cotton Fabrics | 5, 10, 25, 50, 100 | Up to 30% reduction max | Plain weave is more susceptible |
| Cotton/Polyester Blend | 5, 10, 25, 50, 100 | Up to 20% reduction max | Slightly better retention, less recyclable |
Cotton fabric stands up to repeated washing and daily use, making it a reliable choice for clothing, bedding, and DIY projects.
Absorbency
One of the standout properties of cotton fabric is its absorbency. Cotton can soak up 24-27 times its weight in water. This makes it perfect for towels, bathrobes, and summer clothes. Lab tests measure absorbency by checking how much water cotton fabric can hold and how quickly it wicks moisture.
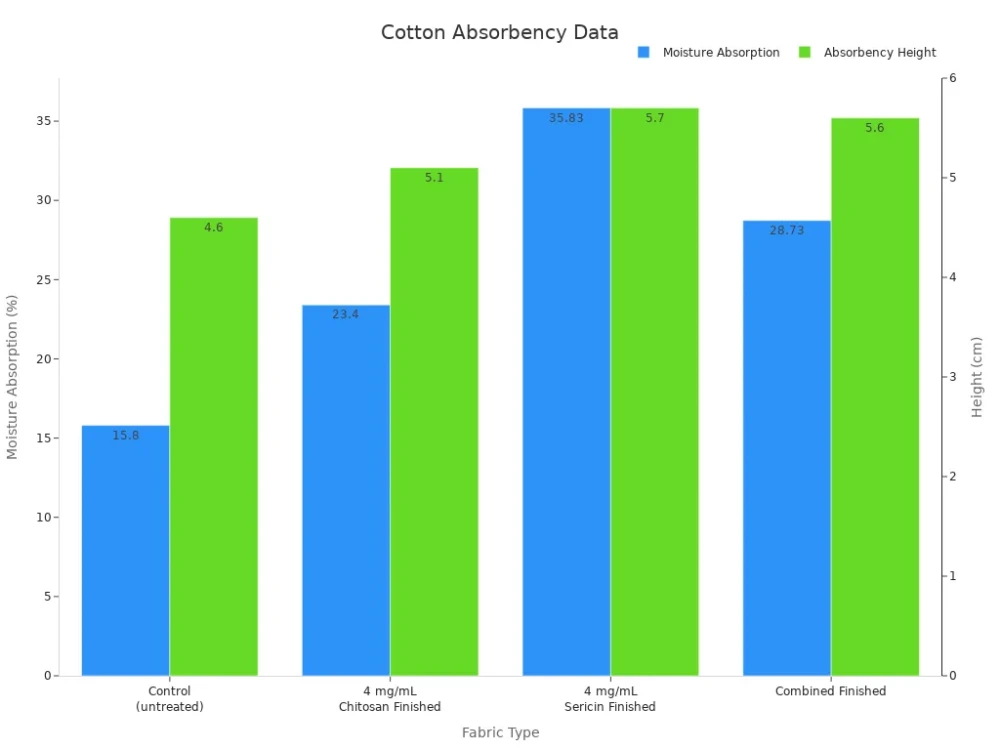
You can see from the chart that finishing treatments can boost absorbency even more. Cotton fabric’s ability to absorb moisture keeps you dry and comfortable, especially in hot weather.
The properties of cotton fabric—softness, breathability, durability, and absorbency—make it a favorite for so many uses. When you choose cotton, you get comfort and performance in every project.
Cotton Fabric Types
Common Types

When you start exploring cotton fabric, you’ll notice there are many different types of cotton fabric, each with its own feel and use. Let’s look at some of the most popular cotton fabric varieties you’ll find in stores and online:
- Muslin: This lightweight, soft cotton fabric feels airy and gentle. You often see muslin in summer clothes, baby items, and even as a base for sewing patterns. It absorbs moisture well and dries quickly. Muslin’s crinkled look gives it a relaxed, elegant style.
- Poplin: Poplin is a compact, smooth cotton fabric. It’s non-stretch, opaque, and has a nice weight (about 196 g/m²). You’ll love poplin for shirts, dresses, and crafts because it’s easy to sew and holds its shape. Care is simple—wash gently at 30°C and iron at medium heat.
- Denim: Denim is a sturdy cotton fabric, famous for jeans and jackets. It’s woven in a twill pattern, making it strong and long-lasting. Denim works well for clothing that needs to handle daily wear.
- Sateen: Sateen uses a special weave to create a soft, smooth surface with a gentle sheen. You’ll find sateen in bedding and fancy shirts. It feels silky but is still 100% cotton.
F&A offers a wide range of cotton fabric varieties, from classic muslin and poplin to custom prints inspired by Chinese heritage and modern trends. You can even design your own fabric with F&A’s custom service, making your projects truly unique.
Differences

You might wonder what sets these different types of cotton fabric apart. The answer comes down to how each fabric is made and what it’s best for.
Technical tests show that cotton blends and weaves change the fabric’s thickness, flexibility, and drape. For example, muslin is light and airy, perfect for summer, while denim is thick and tough, great for winter wear.
- Cotton/elastane blends manage moisture better and dry faster than pure cotton.
- Poplin stays crisp and smooth, while muslin feels soft and flows easily.
- Sateen drapes beautifully and has a subtle shine, making it ideal for special occasions.
| Fabric Type | Weight/Feel | Best Use | Care Tips |
|---|---|---|---|
| Muslin | Light, airy | Summer wear, baby items | Wash cool, air dry |
| Poplin | Smooth, compact | Shirts, crafts | Gentle wash, iron medium |
| Denim | Heavy, durable | Jeans, jackets | Wash inside out, line dry |
| Sateen | Soft, shiny | Bedding, dress shirts | Gentle wash, low iron |
Today, many people want a cotton fabric that tells a story. Heritage-inspired designs, like those in F&A’s in-house collection, blend traditional Chinese patterns with modern style. This trend adds meaning and beauty to your DIY projects. You get both quality and a touch of culture in every yard.
Uses and Care
Everyday Uses
You probably see cotton fabric everywhere in your daily life. It’s a staple for clothing, home textiles, and even accessories.
Cotton feels soft and breathable, which makes it perfect for T-shirts, jeans, dresses, and pajamas. You’ll also find cotton in bed sheets and towels, curtains, and upholstery. These items stay popular because the cotton fabric is gentle on your skin and holds color well.
Check out how people use cotton every day:
| Application Sector | Everyday Applications | Key Consumer Trends |
|---|---|---|
| Apparel | T-shirts, jeans, dresses, pajamas | Comfort and sustainability matter |
| Home Textiles | Bed sheets, towels, curtains, upholstery | Natural, hypoallergenic materials |
| Accessories | Bags, hats, scarves | Style meets function |
| Industrial Textiles | Medical supplies, workwear, art canvas | Durability and eco-friendly choices |
Cotton’s share in retail apparel and home furnishings has grown from 34% in the 1970s to over 60% today. The common uses for cotton keep expanding as people look for comfort and sustainability in their everyday products. When you choose cotton fabric, you join a global trend that values both tradition and innovation.
Environmental Impact
You might wonder, how does cotton fabric impact the environment? The answer depends on how the cotton is grown and processed. Organic cotton and eco-friendly alternatives help protect the environment by avoiding harmful chemicals and using less water.
Organic farms use crop rotation, natural pest control, and compost to keep the soil healthy. These methods lower greenhouse gas emissions and support biodiversity.
- Organic cotton farming avoids synthetic pesticides and fertilizers.
- Water use drops by up to 91% compared to conventional cotton.
- Certifications like GOTS, OEKO-TEX, and BCI ensure safe, sustainable practices.
- The U.S. Cotton Trust Protocol tracks water, energy, and emissions, offering real proof of sustainability.
Sustainability and cotton fabric go hand in hand when you choose certified options. F&A supports these efforts by offering fabrics that meet strict environmental standards. If you care about how cotton fabric impacts the environment, look for these certifications and choose brands that value transparency.
Care Tips
Taking care of cotton fabric is easy. You can wash most cotton items in cool or warm water. Use a gentle detergent and avoid harsh bleach. For best results, air dry or tumble dry on low. Iron on medium heat if needed. These simple steps help your cotton fabric last longer and keep its softness.
Tip: Always check the care label before washing. Some cotton fabrics, like poplin or sateen, may need special attention to keep their shape and shine.
The uses of cotton fabric go far beyond clothing. You’ll find it in crafts, home décor, and even DIY projects. With the right care, your cotton items will stay beautiful and comfortable for years. When you choose cotton, you support sustainability and enjoy the many benefits of this timeless material.

Conclusion
You’ve seen how cotton fabric starts as a humble plant and becomes a staple in your life. Cotton stands out for its comfort, strength, and ability to adapt to so many uses.
You can find cotton in flannel, denim, muslin, and sateen, each offering something unique. Cotton fabric breaks down quickly in nature, unlike synthetics, so it helps keep the planet cleaner.
- Upcycling, organic farming, and digital printing make cotton even better for DIY projects.
- You can choose cotton fabric for clothing, crafts, or home décor and know you’re making a smart, sustainable choice.
If you want to start a creative journey, F&A gives you quality cotton and inspiration. You can do this—just pick your favorite cotton fabric and let your ideas grow!
FAQ
What makes cotton fabric good for beginners?
Cotton fabric is easy to cut, sew, and press. You can handle it without much trouble. It does not slip around like silk or stretch like knits. If you are just starting out, cotton helps you learn the basics with less frustration.
Can I wash cotton fabric in a washing machine?
Yes, you can! Most cotton fabrics handle machine washing well. Use cool or warm water and a gentle cycle. Always check the care label first. Air drying keeps your cotton soft and helps it last longer.
Does cotton fabric shrink after washing?
Cotton can shrink a little the first time you wash it. To avoid surprises, wash and dry your cotton fabric before you start your project. This step, called pre-washing, helps your finished item keep its shape.
Is cotton fabric safe for sensitive skin?
Absolutely! Cotton feels soft and gentle. It does not trap heat or irritate most skin types. Many people with allergies or sensitive skin choose cotton for clothing, bedding, and baby items.
How do I keep the cotton fabric looking new?
Tip: Wash cotton in cool water and avoid harsh bleach. Iron on medium heat if needed. Store your cotton items in a dry place. These steps help your fabric stay bright, soft, and fresh.
