You might wonder, How is cotton fabric made? The journey starts with the cotton plant and moves through several steps—cotton cultivation, harvesting, ginning, carding, spinning, weaving or knitting, and finishing.
When you ask how cotton is made into fabric, you follow a path shaped by both tradition and modern technology.
These steps matter if you care about quality, sustainability, or enjoy DIY projects. Cotton production stands at the heart of the textile world, with over 38% of the global textile market revenue coming from cotton. The main producing countries—China, India, the U.S., and others—grow more than 95% of the world’s cotton.
| Statistic Description | Value / Detail |
|---|---|
| Cotton revenue share in the textile market (2023) | Over 38% of the overall revenue share |
| Major cotton-producing countries | China, India, U.S., Brazil, Pakistan, Australia, Cameroon, Côte d’Ivoire |
| Industry-grade cotton production concentration | More than 95% growth in the above countries |
| Asia Pacific region revenue share (2023) | Over 53% |
| Global textile market size (2023) | USD 1,837.27 billion |
| Projected market size (2030) | USD 3,047.23 billion |
| CAGR (2024-2030) | 7.4% |
| Dominant fiber type | Natural fibers, especially cotton, due to superior properties (strength, absorption, color retention) |
| Leading application segment | Fashion and apparel |
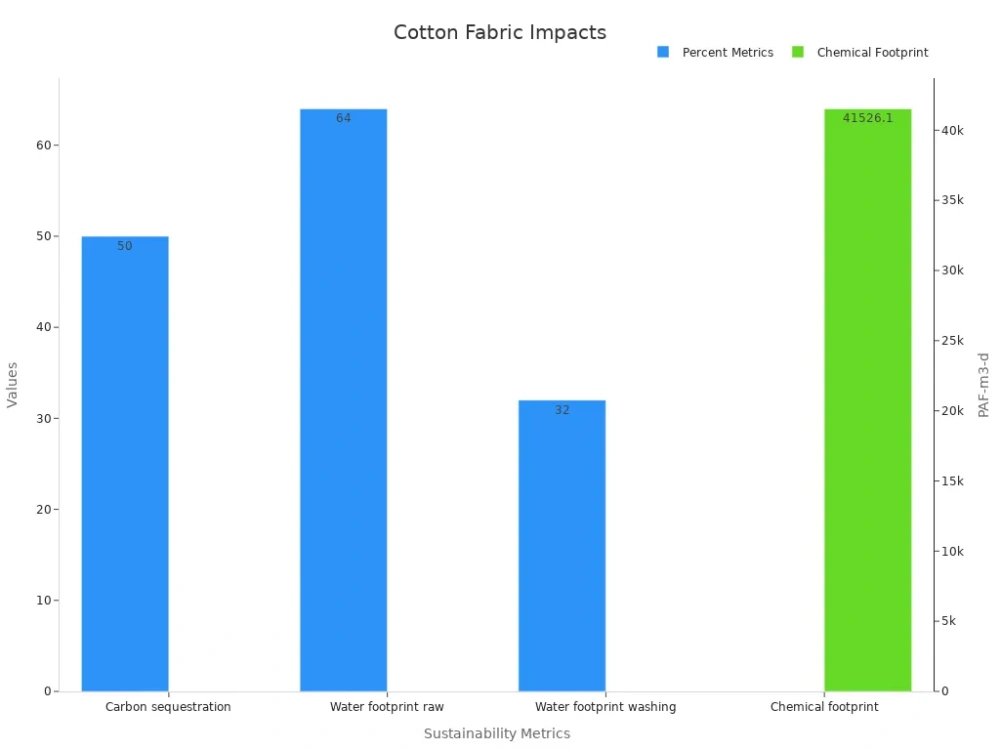
You see the impact of how cotton is made into fabric, not only in clothing and home décor but also in the environment. As you explore how cotton fabric is made, consider the following chart, which highlights the sustainability metrics of cotton manufacturing:
Key Takeaways
- Cotton fabric is made through a step-by-step process starting from planting cotton seeds to finishing the fabric with dyeing and printing.
- High-quality cotton fibers and precise manufacturing steps like carding, spinning, weaving, and knitting shape the strength and feel of the fabric.
- Different cotton types and fabric weaves offer various textures and uses, from soft luxury fabrics to durable workwear materials.
- Eco-friendly practices and advanced technology help reduce environmental impact while keeping cotton fabric strong and beautiful.
- F&A supports custom cotton fabrics with strict quality control, making it easy for DIY enthusiasts to create unique and sustainable projects.
Cotton Production Process

Cultivation & Harvesting
You start the cotton production process with cotton cultivation. Farmers plant high-quality seeds in warm, moist soil. The cotton plant grows through several stages, each with unique needs. The table below shows the main stages and best practices:
| Stage Name | Duration | Key Activities | Best Practices |
|---|---|---|---|
| Germination | 4–10 days | Root and shoot emerge | Use quality seeds, keep soil moist |
| Seedling Establishment | Up to 10 days | Roots and leaves develop | Monitor pests, balance nutrients |
| Vegetative Growth | 2–5 weeks | Leaves and stems grow | Fertilize, control weeds |
| Square Formation | ~3 weeks | Flower buds appear | Irrigate, check for pests |
| Flowering | ~3 weeks | Flowers open and pollinate | Support pollinators |
| Boll Development | ~55 days | Bolls grow, fibers form | Regular irrigation, pest control |
| Maturation/Harvest | 20–30 days | Bolls open, fibers dry | Harvest at the right time |
You can see that cotton cultivation lasts about 160–180 days. Farmers use new planting patterns and densities to boost yield. For example, four-row, low-density planting can increase water productivity by up to 13.4%.
Many fields now use transgenic hybrids for better output. When you ask how cotton is picked, you find both hand and machine harvesting. Modern farms use UAVs and LiDAR to predict yields and improve efficiency.
Ginning & Cleaning
After harvesting, you move to cotton processing. Ginning separates the cotton fibers from seeds. Early gins like Eli Whitney’s changed the industry by making this step faster. Today, advanced gins use robotic arms, sensors, and computerized controls.
These machines clean cotton several times faster than older methods. Multi-stage cleaning removes dirt and debris with air currents, magnetic separators, and optical sorters. Air blast separation protects delicate fibers. Modern gins also use dust control and energy-saving systems, showing a focus on sustainability.
F&A uses state-of-the-art ginning and cleaning equipment to ensure high-quality fibers for textile manufacturing.
Carding & Spinning
Next, you enter the carding and spinning steps. Carding untangles and aligns the cotton fibers, making them smooth and ready for spinning. Spinning twists these fibers into strong yarn. F&A’s advanced machinery handles these tasks with precision.
This stage is key in the textile manufacturing process because it affects the strength and feel of the final fabric. High-quality carding and spinning lead to better cotton fabrics for your DIY projects.
How is Cotton Fabric Made?
Weaving & Knitting
You see the transformation from yarn to fabric in two main ways: weaving and knitting. These methods shape how cotton is made into fabric and determine the final look and feel.
Weaving interlaces two sets of yarns at right angles. This process creates strong, stable fabrics like woven cotton fabric, which you often find in shirts, dresses, and home décor. Knitting, on the other hand, loops yarns together. This method produces stretchier, softer fabrics, perfect for T-shirts and activewear.
Modern textile manufacturing uses advanced machinery to speed up these processes. For example, weaving machines can reach speeds of up to 1,000 wefts per minute. This high speed allows for efficient production of woven cotton fabric without sacrificing quality.
Knitting machines, especially those used for sweaters, have seen rapid growth. The market for sweater knitting machines is expected to grow at a 5.5% annual rate, reaching $730 million by 2032.
This growth comes from new technology that lets you control stitch length, pattern, and yarn type, giving you fabrics with precise stretch and strength.
| Textile Technology | Production Speed | Mechanical Strength | Mechanical Stretch |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weaving | Up to 1,000 wefts/min | High | Low |
| Braiding | Up to 58 rounds/min | High | Low |
| Weft-knitting | Up to 40 rounds/min | Low | High |
F&A uses over 1,000 airjet looms for large-scale fabric manufacturing. These looms produce consistent, high-quality cotton fabrics for a wide range of uses. The company’s advanced knitting machines allow for custom patterns and textures, meeting the needs of both traditional and modern DIY projects.
The quality of the final cotton fabric depends on the properties of the cotton fibers and the precision of the manufacturing process. For example, the famous Dhaka muslin was prized for its fine, mature fibers and expert spinning.
Today, you benefit from scientific advances that let manufacturers analyze fiber maturity and structure, ensuring strong, smooth yarns for both woven and knitted fabrics.
Finishing Techniques
Once you have the fabric, you move to finishing techniques. These steps give the fabric its final appearance, texture, and performance. Finishing includes scouring, bleaching, dyeing, printing, softening, and preshrinking.
Each step in cotton fabric manufacturing changes the fabric’s surface and chemical properties, making it ready for use.
Scouring removes natural waxes and impurities from the cotton, increasing the fiber’s surface activity. For example, after scouring, the zeta potential of cotton shifts from -12.2 mV to -13.4 mV, showing that the fibers are cleaner and more ready to absorb dyes.
Bleaching further whitens the fabric, while dyeing and printing add color and patterns. F&A uses both screen printing and high-speed digital printing. Digital printing allows for complex, multi-color designs with sharp detail, perfect for custom projects.
Finishing also includes processes like mercerizing, which strengthens the fabric and improves dye uptake, and sanforizing, which reduces shrinkage. F&A’s advanced finishing lines use energy-efficient methods to save resources and maintain high quality.
For example, by optimizing the finishing process and omitting certain steps like heat-setting, manufacturers can increase productivity by up to 38% and reduce energy use by 40%, all while keeping fabric quality high.
| Aspect | Regular Process Details | Experimental Process Details | Impact / Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Finishing Steps | Brushing – Singeing – Desizing – Mercerizing – Heat set – Softening – Drying – Sanforizing | Brushing – Desizing – Mercerizing – Softening – Drying – Sanforizing (Singeing and Heat set omitted) | Process optimization by omitting singeing and heat-setting |
| Productivity Improvement | Baseline | Increased by 33-38% | Significant productivity gain |
| Energy Consumption Reduction | Baseline | Reduced by 34-40% | Major energy savings |
| Specific Energy Savings | N/A | 1235 kW power and 1947.5 m³ natural gas saved for 20 km of fabric (heat-setting omitted) | Quantified energy savings in the heat-setting process |
| Fabric Quality Impact | N/A | No detrimental effects on fabric quality (tested parameters: drape, stiffness, tear strength, dimensional stability) | Maintained fabric quality despite process changes |
| Payback Period for Optimization | N/A | Approximately 4 months | Economic feasibility of process changes |
F&A’s professional inspection team checks every yard of fabric to ensure it meets strict ISO standards. You receive cotton fabric that looks great, feels soft, and lasts through many uses.
When you ask how cotton is made into fabric, you see a journey that starts with raw cotton and ends with a finished product ready for your next creative project.
Each step in the process, from spinning to finishing, shapes the quality and sustainability of the cotton fabric you use. F&A’s commitment to advanced technology and careful quality control ensures you get the best results for your DIY and fashion projects.
Types of Cotton & Fabrics
Cotton Varieties
You can find several main types of cotton grown around the world. Each variety has unique qualities that affect the fabric you use in your projects. The most common type is Gossypium Hirsutum, also called Upland cotton.
This variety makes up over 90% of global production. It has short to medium fibers and works well for everyday clothing and fast fashion.
If you want something softer and more luxurious, you might choose Gossypium Barbadense. This group includes Pima, Supima, Egyptian, and Sea Island cotton. These types have extra-long fibers, which give the fabric a silky feel and extra strength. They make up less than 5% of the market but are popular for luxury fabrics.
Other types, like Gossypium Arboreum and Gossypium Herbaceum, have shorter, coarser fibers. You often see these in traditional or rugged fabrics. The table below shows how these cotton types compare:
| Cotton Type (Scientific Name) | Fiber Length (mm) | Quality | Market Share | Typical Uses | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gossypium Barbadense | >35 | High (fine, soft, durable) | <5% | Luxury fabrics | High to very high |
| Gossypium Hirsutum | 20-30 | Medium | >90% | General textiles, fast fashion | Low |
| Gossypium Arboreum | 25-26 | Variable, coarse | <2% | Rugged, wool-like fabrics | Unknown |
| Gossypium Herbaceum | 20-25 | Variable, coarse | <2% | Traditional hand-woven fabrics | Unknown |
Tip: Longer cotton fibers create softer and more durable fabrics. Extra-long staple cotton is best for premium projects.
Regional and genetic factors also shape cotton quality. For example, cotton grown in warmer regions may have higher cellulose or wax content, which changes how the fiber feels and performs. Breeding programs focus on both fiber quality and adaptability to local climates.
Fabric Types
You can choose from many fabric types made from cotton, each with its own texture and use. Some fabrics feel soft and smooth, while others are thick and warm. The way the cotton is spun and woven, or knitted changes the final product.
Here is a table that shows some popular cotton fabric types and their features:
| Fabric Type | Construction/Weave | Key Properties | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cotton Satin | Fine thread, woven | Silky, smooth, soft | Bedding, luxury clothing |
| Percale Cotton | Tight weave, 100% cotton | Crisp, cool, pleasant feel | Sheets, shirts |
| Jersey Cotton | Knitted, flexible | Stretchy, soft, lightweight | T-shirts, dresses |
| Flannel | Finely woven, roughened | Warm, woolly, thick | Pajamas, blankets |
| Twill Cotton | Diagonal weave | Durable, strong, thick | Jeans, workwear |
| Renforcé Cotton | Special weaving technique | Firm, durable, smooth | Bedding, children’s clothes |
| Combed Cotton | Short fibers removed | Higher quality, longer-lasting | Premium apparel, towels |
You can also find organic cotton, which is grown with less environmental impact. This type focuses on sustainability rather than fiber length or softness.
Note: When you select a cotton fabric, think about the fiber length, weave, and finish. These factors decide how your finished project will look and feel.
Sustainability & Innovation
Eco-Friendly Practices
You play a key role in supporting eco-friendly cotton fabric production. F&A leads the way by using renewable energy, water-saving dyeing methods, and recycled fibers. These steps help reduce the environmental impact of every yard of fabric you use.
Many factories now replace coal with solar or wind power. Waterless dyeing techniques cut down on water and chemical pollution. F&A partners with suppliers who provide organic and recycled cotton, making your fabric choices better for the planet.
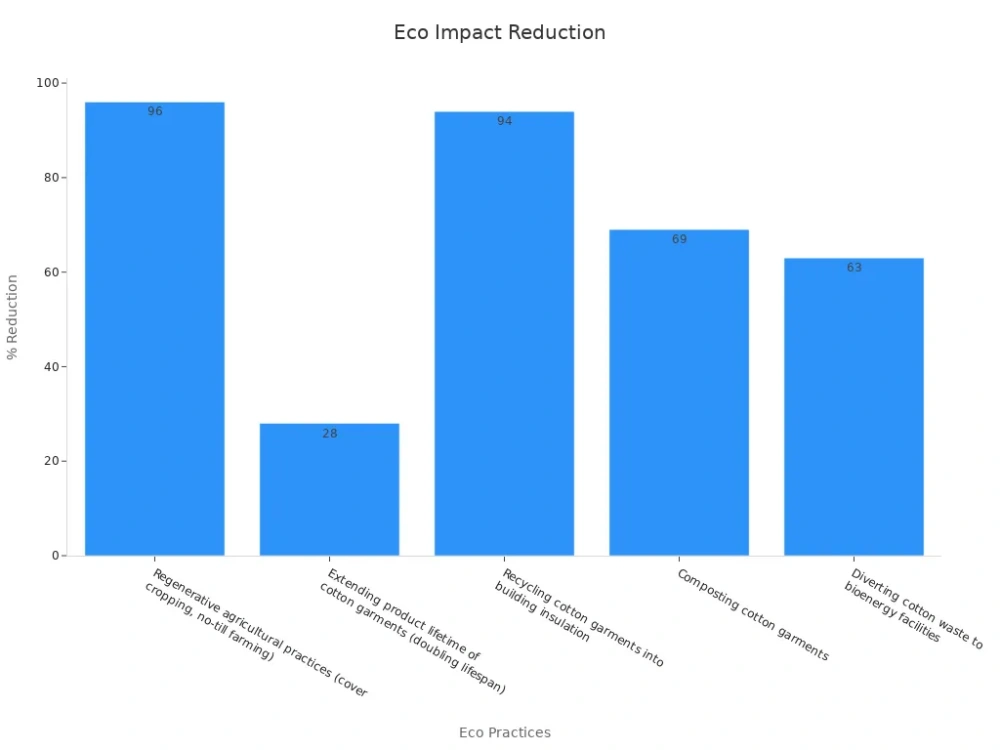
Here are some eco-friendly practices and their impact:
| Eco-Friendly Practice | Quantified Reduction in Environmental Impact (10 years) |
|---|---|
| Regenerative farming (cover crops, no-till) | 96% reduction |
| Doubling garment lifespan | 28% reduction |
| Recycling cotton into insulation | 94% reduction |
| Composting cotton garments | 69% reduction |
| Using cotton waste for bioenergy | 63% reduction |
You can see how these changes make a real difference. Regenerative agriculture, for example, almost eliminates soil loss and boosts soil health. Recycling and composting cotton garments keep waste out of landfills.
F&A’s modern facilities use energy-efficient equipment and advanced recycling systems. These innovations help save water, energy, and raw materials. You benefit from fabrics that are both high-quality and environmentally responsible.
Ethical Production
You want to know that your cotton fabric comes from ethical sources. F&A meets strict standards for fair labor and safe working conditions. The company supports certifications like OEKO-TEX, GOTS, and the Better Cotton Initiative. These programs check for fair wages, safe workplaces, and responsible farming.
Many leading brands, such as Patagonia and Levi’s, also use organic and recycled cotton. They commit to fair labor and transparent supply chains. F&A follows these best practices by auditing suppliers and choosing partners who share these values.
When you choose F&A, you support a brand that values both people and the planet. You help build a future where cotton fabric is made with care, innovation, and respect for everyone involved.
How is Cotton Turned into Fabrics?

Customization & Applications
You can see how cotton is turned into fabrics that fit many creative needs. When you ask how cotton is made into fabric, you find that the process shapes the final product for different uses. In fashion, designers use cotton fabric for clothing lines that focus on comfort, breathability, and sustainability.
Home décor projects, such as quilts, pillow covers, and curtains, rely on cotton for its softness and durability. DIY enthusiasts often choose cotton for tote bags, art projects, and upcycled crafts because it is easy to work with and holds color well.
The transformation from cotton fiber to finished fabric depends on key textile metrics. Thread count and yarn count control the softness, thickness, and strength of the fabric.
Technologies like DNA markers and Permanent Bale Identification tags help track cotton from farm to finished product. These tools ensure you get authentic, high-quality cotton fabric for your projects.
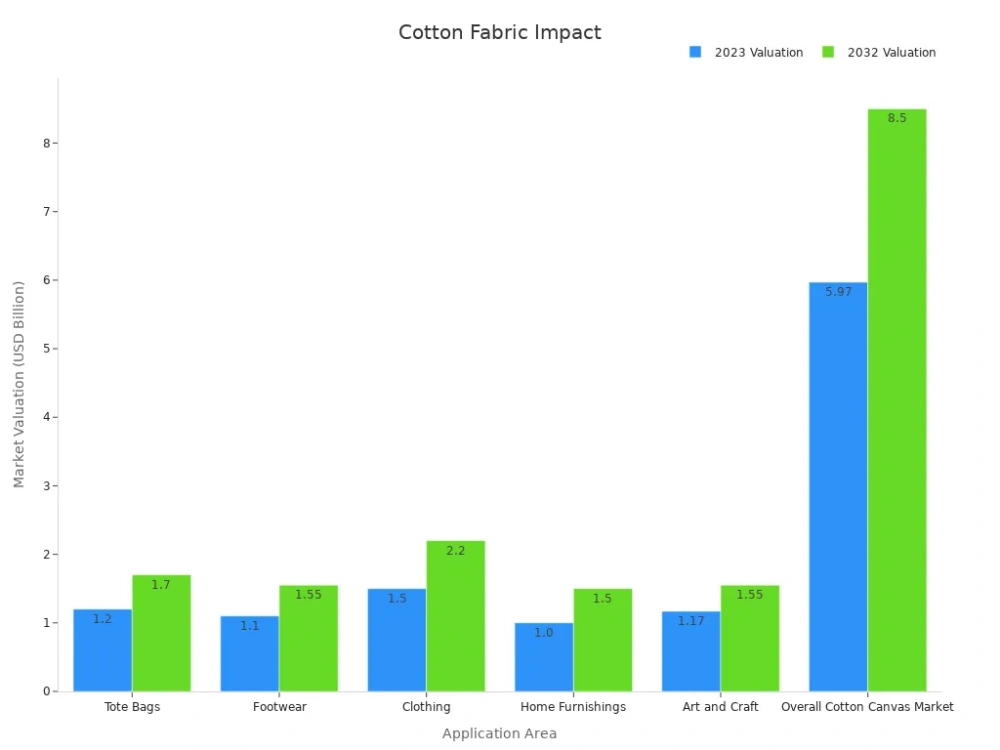
The market for customized cotton applications keeps growing. Quilting and crafting communities drive demand for unique, personalized items. Upcycled cotton fabrics are popular for eco-friendly home textiles and creative DIY projects. The table below shows how different application areas are valued in the market:
| Application Area | Market Valuation 2023 (USD Billion) | Projected Valuation 2032 (USD Billion) | Key Impact Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tote Bags | 1.2 | 1.7 | Popular for sustainable, reusable products |
| Footwear | 1.1 | 1.55 | Growth driven by demand for breathable, casual footwear |
| Clothing | 1.5 | 2.2 | Fashion designers focus on sustainable clothing lines |
| Home Furnishings | 1.0 | 1.5 | Durable, aesthetic cotton textiles for home décor |
| Art and Craft | 1.17 | 1.55 | Strong DIY and crafting community demand |
| Overall Cotton Canvas Market | 5.97 | 8.5 | Reflects growing consumer preference for eco-friendly cotton products across sectors |
F&A’s Role in DIY Fabric Market
You play a key role in shaping how cotton is made into fabric for modern DIY projects. F&A stands out by offering a wide range of cotton fabrics designed for crafters, quilters, and home décor lovers.
You can choose from traditional Chinese-inspired prints or modern patterns, all produced with advanced technology and strict quality control.
F&A’s custom fabric service lets you bring your ideas to life. You can upload your designs and receive high-quality cotton fabric tailored to your needs. This service supports both small DIY projects and large-scale collaborations.
Major retailers like Walmart, Disney, Joann, and ALDI trust F&A for their fabric needs, showing the brand’s reputation for quality and reliability.
When you explore how cotton is turned into fabrics, you see that F&A uses traceability systems and precise textile metrics to ensure every yard meets your expectations. Whether you want fabric for clothing, home décor, or creative crafts, F&A helps you create unique, sustainable projects that reflect your style.
Conclusion
You have seen how cotton travels from plant to finished fabric through careful steps. Quality and sustainability shape every stage.
- Cotton Incorporated supports hundreds of research projects each year, improving yields and eco-friendly practices.
- Labs test fiber strength, color, and durability, while new finishes boost performance and comfort.
- Programs like the U.S. Cotton Trust Protocol track progress in reducing carbon emissions and promoting better farming.
When you choose cotton fabric, you support both tradition and innovation. F&A offers you high-quality, sustainable, and customizable cotton fabrics for your next creative project.
FAQ
What makes cotton fabric a good choice for DIY projects?
Cotton fabric feels soft, breathes well, and holds color. You can cut and sew it easily. It works for clothing, crafts, and home décor. F&A offers many patterns and custom options, so you can find the perfect fabric for your project.
How does F&A ensure the quality of its cotton fabrics?
F&A uses advanced machines and a skilled inspection team. Every yard of fabric meets strict ISO standards. You receive fabric that looks great, feels soft, and lasts through many uses.
Can I order custom cotton fabric designs from F&A?
Yes! You can upload your design to F&A’s website. The team prints your pattern on high-quality cotton fabric using digital technology. You get a unique fabric made just for you.
Is cotton fabric eco-friendly?
Cotton is a natural fiber. F&A uses eco-friendly practices, such as water-saving dyeing and renewable energy. You help the planet when you choose cotton fabrics made with these methods.



